Is your body trying to tell you something? An overactive thyroid, or hyperthyroidism, can sneak up on you, often masquerading as other minor ailments. Recognising the early warning signs is crucial for effective management and a better quality of life. This list outlines 21 potential symptoms. Remember, this information is for educational purposes only, and a doctor's visit is essential for diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Hyperthyroidism: 21 Early Warning Signs
Many people ignore the early signs of an overactive thyroid. These symptoms are often subtle and easily mistaken for stress or other minor health issues. Do any of these sound familiar?
Unexplained Weight Loss: Noticeable weight loss despite a normal or even increased appetite. Your metabolism is working overtime, burning calories faster than usual. This isn't necessarily a good thing, however, as unexplained weight loss can be linked to other underlying illnesses.
Fatigue and Weakness: Feeling constantly tired, even after a good night's sleep? Your body is working overtime, and it's taking its toll.
Rapid or Irregular Heartbeat (Palpitations): A racing heart or a fluttering feeling in your chest? This is often an early warning sign. Don't dismiss it as mere stress; it could indicate something more serious.
Increased Heat Sensitivity: Feeling too warm, even in cooler environments? Your thyroid might be producing excess hormones, making you more sensitive to heat than usual.
Irritability, Anxiety, and Nervousness: Unexplained mood swings of anxiety, nervousness, or irritability? Your thyroid can affect your mood and emotional stability. It's important to differentiate between normal emotions and something that might have an underlying medical cause.
Tremors (Shaking): Slight shaking, especially in your hands? Your thyroid hormones can affect your nervous system. This might be subtle, but it's still a sign not to ignore.
Muscle Weakness: Unexpected muscle weakness and fatigue are often overlooked. This is a sign that deserves attention.
Changes in Bowel Habits: Shifting from constipation to diarrhoea? This could be a sign of an overactive thyroid. Your digestive system is sensitive to hormonal imbalances.
Sleep Disturbances: Trouble sleeping through the night? Your body's internal clock might be affected by your overactive thyroid. It's important to consider other potential causes, such as sleep apnoea, but it could indeed indicate a thyroid problem.
Concentration Problems: Finding it difficult to focus on tasks or follow conversations? This can be a sign of an overactive thyroid.
Skin Changes: Noticeable changes in your skin, such as increased sweating or thinner skin? Changes in your thyroid can affect your skin, hair, and nails.
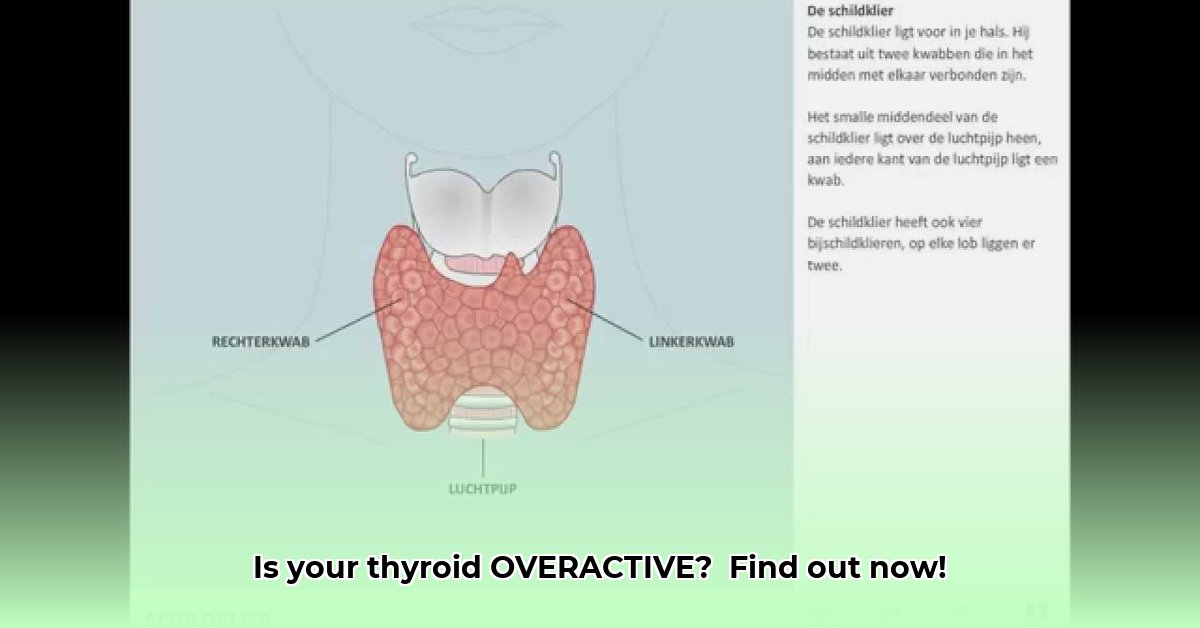
Enlarged Thyroid (Goitre): In some cases, you might notice a noticeable swelling in your neck.
Less Common, but Still Important, Symptoms
While the above symptoms are more common, several others can also indicate an overactive thyroid. These include:
Menstrual Irregularities (in women): Changes in your menstrual cycle, such as heavier periods or absence of periods, can be a sign. Note that this symptom also occurs in an underactive thyroid, so consulting a doctor is crucial.
Increased Appetite: The increase in your metabolism might mean you're hungrier than usual. Note that weight loss is a more common symptom than weight gain.
Hair Loss: Thinning or loss of hair can be a symptom of an overactive thyroid. There are many reasons for hair loss, but this is one to consider.
Vision Problems: Eye problems such as double vision or bulging eyes (Graves' ophthalmopathy) are more serious signs and require immediate attention. This is a more serious condition and requires urgent medical treatment.
Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity.
Increased sensitivity to caffeine or other stimulants.
Restlessness and difficulty staying still.
Loss of libido (decreased sex drive).
Fine, brittle hair.
What to Do if You Suspect an Overactive Thyroid
Recognising the symptoms is the first step. If you experience several of the above, it's crucial to take action:
Make an Appointment with Your Doctor: Don't delay. Early diagnosis is key to effective treatment.
Undergo Blood Tests: Your doctor will likely order blood tests to measure your thyroid hormone levels (TSH, T3, and T4). These tests are essential for diagnosis.
Follow Your Doctor's Advice: Discuss treatment options with your doctor; they will create a plan tailored to your needs.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve your quality of life. Don't hesitate – your health is important!